2. Calculate relative abundance
calc_rel_abund.RmdRelative abundance
bubbler takes an ASV table and converts counts to
relative abundances using this simple formula:
Where
is the count of a given ASV, divided by the sum of all ASV counts. This
way, the sum of all relative abundances equal one. bubbler
then tacks on taxonomic information and optionally metadata. By default,
bubbler::bar_plot produces stacked bar plots, which show
the proportional differences of counts between samples.
# 1. make rel_abund
rel_abund <- rel_abund_qiime(counts_q,
taxa_q,
metadata_q,
taxa_level = "Genus")
# 2. modify rel_abund
rel_abund_pool <- rel_abund %>%
# pool taxa so that only the 12 most abundant taxa are displayed
pool_taxa(n_taxa = 12, keep_metadata = TRUE)
# 3. plot rel_abund
rel_abund_pool %>%
bar_plot() +
# facet samples by body site. free_x removes unwanted white space
facet_wrap(~body_site, scales = "free_x" ) 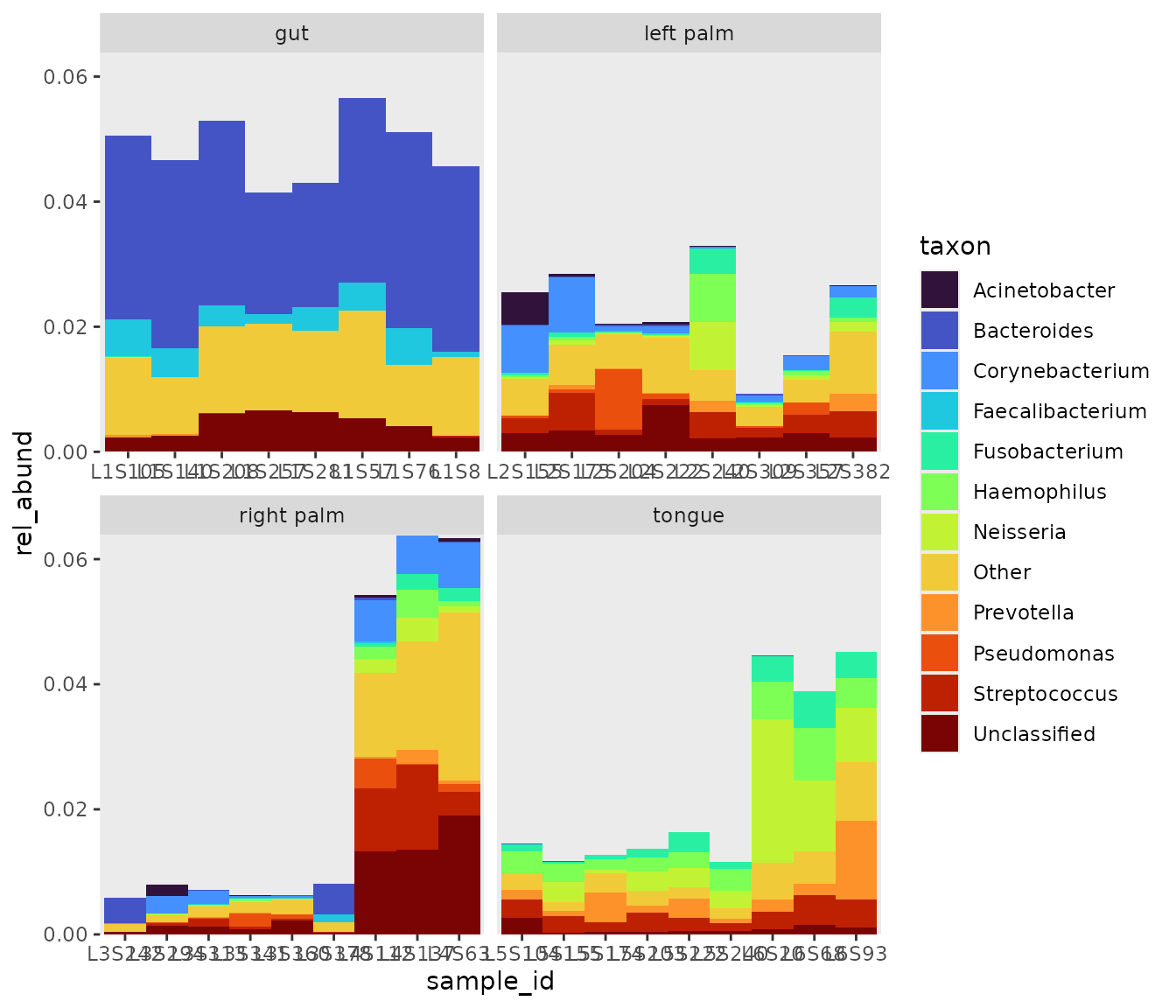
bubbler::bar_plots can also be filled in. Based on the
above plot, subject proportions on the right palm are vastly different,
and this information would be lost in a filled-in bar plot. By filling
the plotting area, we get a better representation of the between-sample
composition, at the cost of obfuscating the between-sample
proportions.
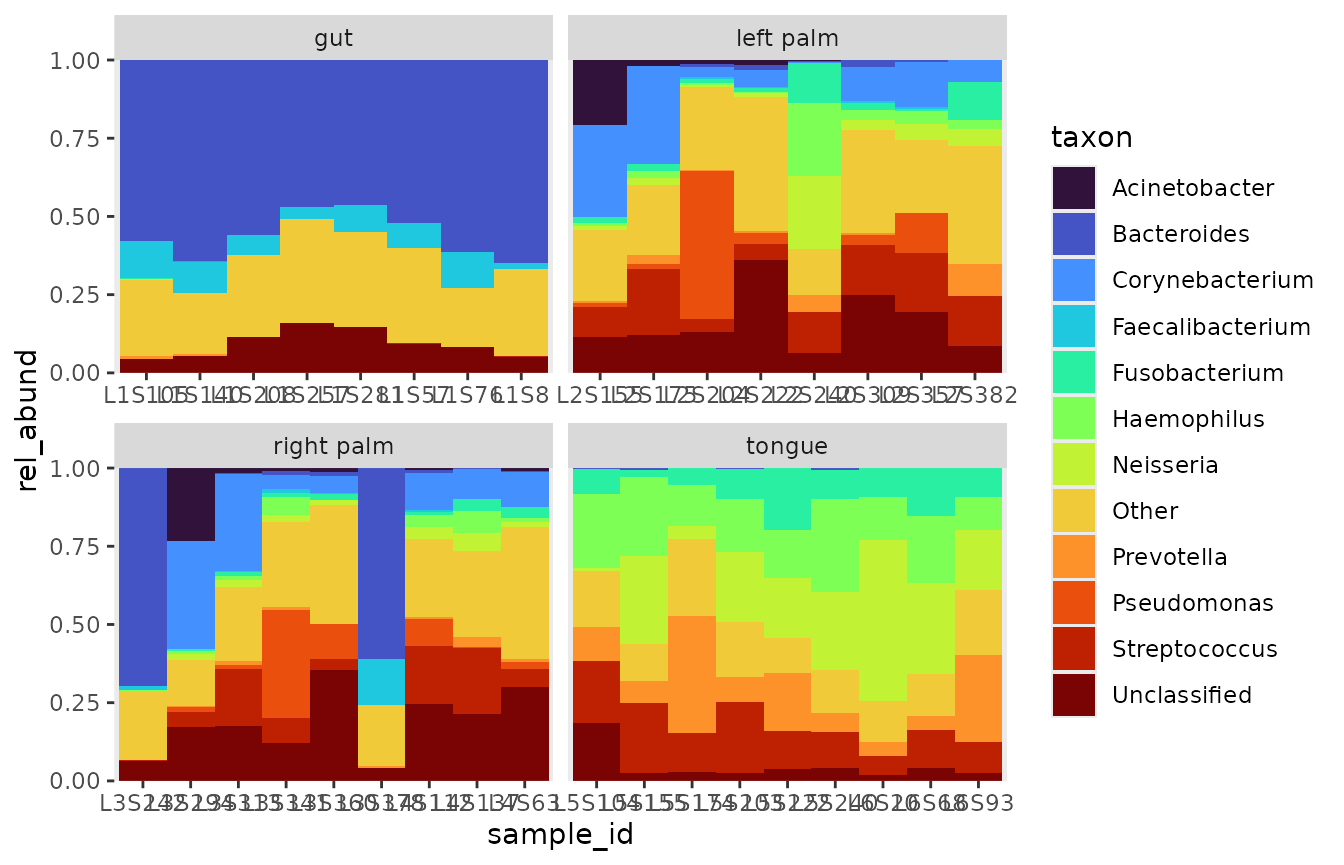
One last thing about relative abundances: when setting
position to “fill”, we are effectively recomputing
rel_abund, so that it sums to one within each bar on the x-axis. This
transformation is equivalent to the following formula:
Where
is the levels of the grouping variable (in this case
sample_id) and
indexs through the ASVs and
indexs through the levels, Within each level of the grouping variable,
the sum of relative abundance equals one, and the total sum of rel_abund
is equal to the
levels. This information is not very important in practice because
position = “fill” scales the relative abundances for
you.
Visualizing variables
bubbler allows you to focus on any metadata variable in
your relative abundance table. Say you wanted to look at relative
abundance across body_site, rather than
sample_id on the x-axis. This can be done by modifying the
x_var argument of bar_plot.
rel_abund_qiime(counts_q, taxa_q, metadata_q, taxa_level = "Genus") %>%
pool_taxa(n_taxa = 12,
keep_metadata = TRUE) %>%
arrange_taxa() %>%
bar_plot(x_var = "body_site")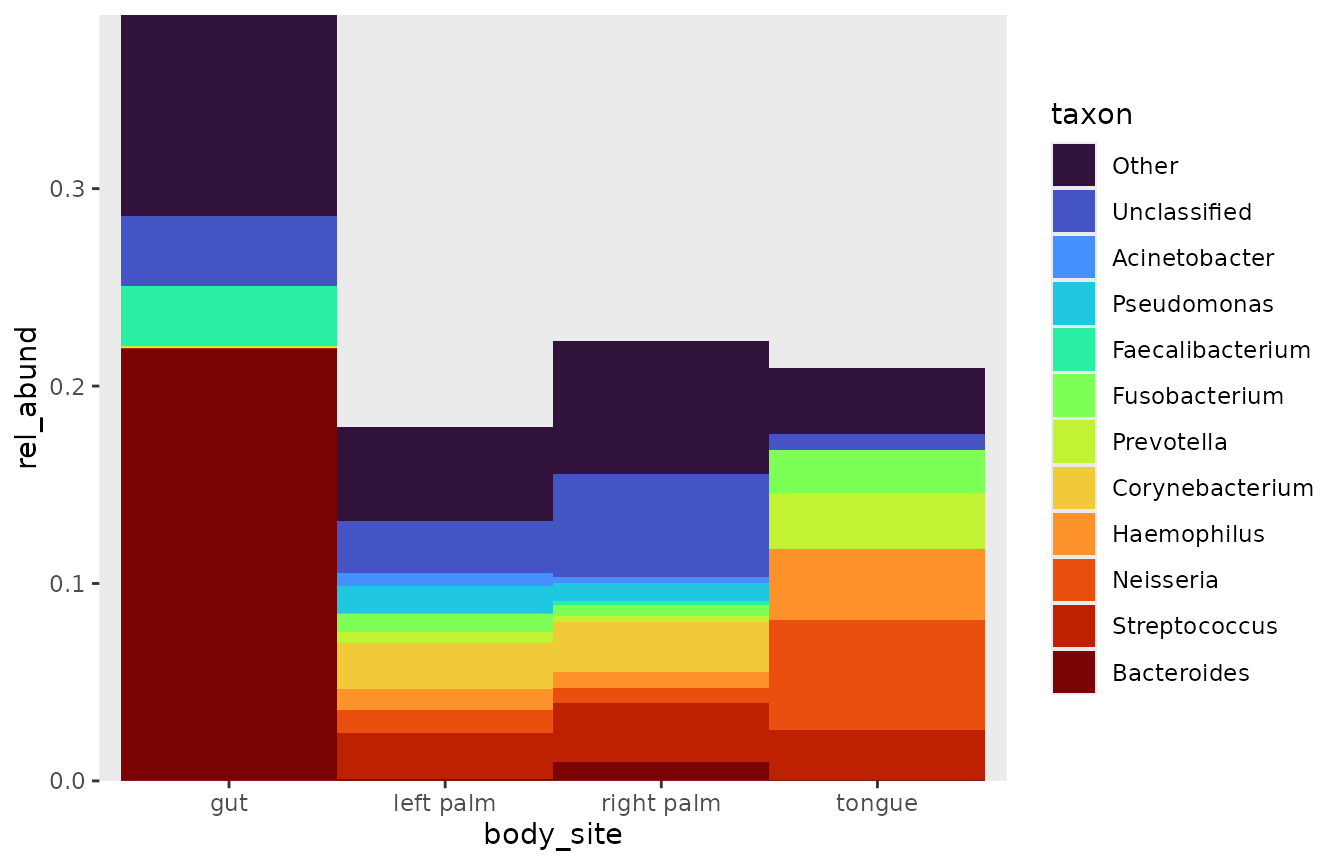
For any given x_var, (sample_id,
body_site, etc ), you have two options for computing the
scaled rel_abund: Setting the var argument within the
rel_abund function, or setting position =
“fill” within bubbler::bar_plot. I prefer the latter
method, which keeps the proportional differences.
# compute in rel_abund
rel_abund_qiime(counts_q, taxa_q, metadata_q,
taxa_level = "Genus",
var = "body_site") %>% # scaling by body_site
pool_taxa(n_taxa = 12,
keep_metadata = TRUE) %>%
arrange_taxa() %>%
bar_plot(x_var = "body_site") # setting body_site as x_var
# scale in plot
rel_abund_qiime(counts_q, taxa_q, metadata_q,
taxa_level = "Genus") %>%
pool_taxa(n_taxa = 12,
keep_metadata = TRUE) %>%
arrange_taxa() %>%
bar_plot(position = "fill", x_var = "body_site") # setting position as fill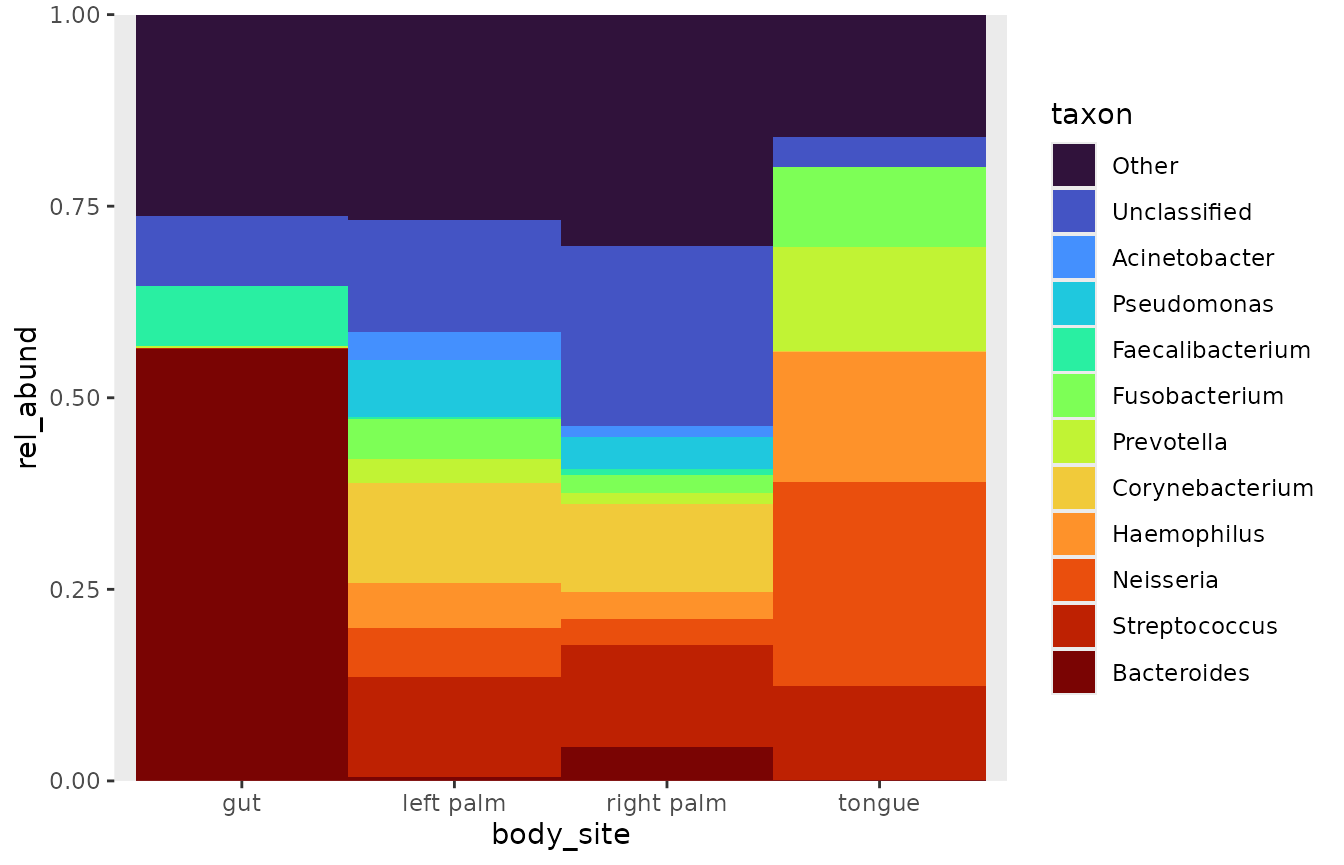
Showing both scaled and unscaled information.
If you want the best of both worlds, you can create a scaled bar plot, and superimpose the proportional abundances. Currently, this feature does not work with a faceting functions, so the only option would be to split a rel_abund table into multiple plots.
# order by sample read abundance, plot as line
library(patchwork)
counts_q <- system.file("extdata", "qiime", "table-dada2.qza", package = "bubbler")
taxa_q <- system.file("extdata", "qiime", "taxonomy.qza", package = "bubbler")
metadata_q <- system.file("extdata", "qiime", "sample-metadata.tsv", package = "bubbler")
q <- rel_abund_qiime(
asv_qiime = counts_q,
taxa_qiime = taxa_q,
metadata_qiime = metadata_q,
taxa_level = "Genus", ) %>%
pool_taxa(n_taxa = 8, keep_metadata = TRUE) %>%
arrange_taxa() %>%
arrange_var(levels = "body_site")
# arrange_var_abund(flip = TRUE)
yes <- subset_rel_abund(q, var = "reported_antibiotic_usage", selection = "Yes")
no <- subset_rel_abund(q, var = "reported_antibiotic_usage", selection = "No")
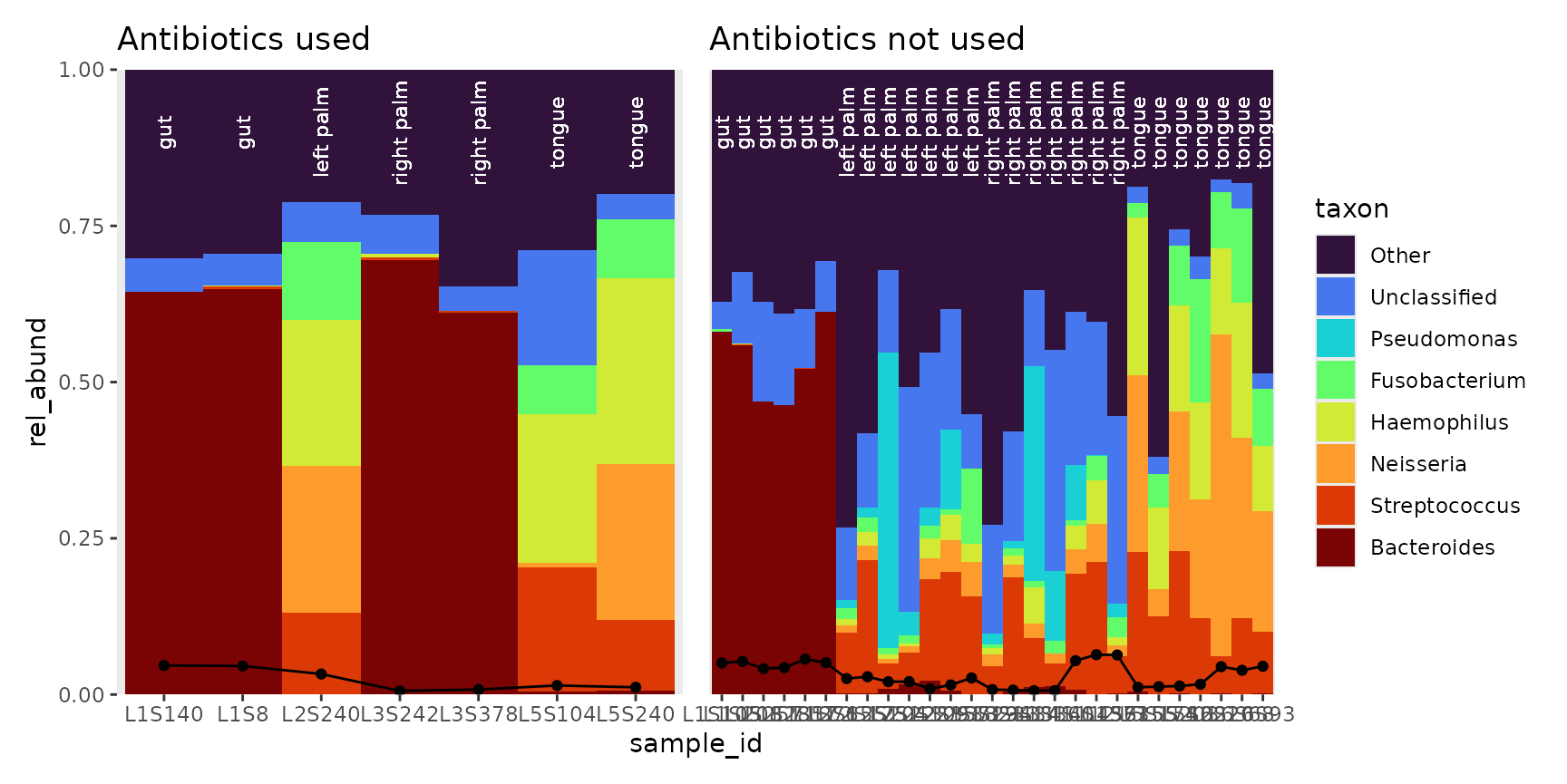
p1 <- bar_plot(yes, position = "fill", true_line = TRUE ) + ggtitle("Antibiotics used") +
geom_text(aes(label = body_site, y = 0.9),
angle = 90, color = "white", size = 3)
p2 <- bar_plot(no, position = "fill" , true_line = TRUE) + ggtitle("Antibiotics not used") +
geom_text(aes(label = body_site, y = 0.9),
angle = 90, color = "white", size = 3)
p1 + p2 + plot_layout(guides = "collect", axes = "collect")